Примечание
Перейти в конец чтобы скачать полный пример кода или запустить этот пример в браузере через JupyterLite или Binder.
Главный собственный вектор Википедии#
Классический способ оценки относительной важности вершин в графе — вычисление главного собственного вектора матрицы смежности, чтобы присвоить каждой вершине значения компонент первого собственного вектора в качестве оценки центральности: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eigenvector_centrality. На графе веб-страниц и ссылок эти значения называются оценками PageRank от Google.
Цель этого примера — проанализировать граф ссылок внутри статей Википедии, чтобы ранжировать статьи по относительной важности согласно этому собственному вектору центральности.
Традиционный способ вычисления главного собственного вектора заключается в использовании метод степенной итерацииbunch
Данные графа извлекаются из дампов DBpedia. DBpedia — это извлечение скрытых структурированных данных из содержимого Википедии.
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import os
from bz2 import BZ2File
from datetime import datetime
from pprint import pprint
from time import time
from urllib.request import urlopen
import numpy as np
from scipy import sparse
from sklearn.decomposition import randomized_svd
Загрузить данные, если они еще не на диске#
redirects_url = "http://downloads.dbpedia.org/3.5.1/en/redirects_en.nt.bz2"
redirects_filename = redirects_url.rsplit("/", 1)[1]
page_links_url = "http://downloads.dbpedia.org/3.5.1/en/page_links_en.nt.bz2"
page_links_filename = page_links_url.rsplit("/", 1)[1]
resources = [
(redirects_url, redirects_filename),
(page_links_url, page_links_filename),
]
for url, filename in resources:
if not os.path.exists(filename):
print("Downloading data from '%s', please wait..." % url)
opener = urlopen(url)
with open(filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(opener.read())
print()
Загрузка файлов перенаправления#
def index(redirects, index_map, k):
"""Find the index of an article name after redirect resolution"""
k = redirects.get(k, k)
return index_map.setdefault(k, len(index_map))
DBPEDIA_RESOURCE_PREFIX_LEN = len("http://dbpedia.org/resource/")
SHORTNAME_SLICE = slice(DBPEDIA_RESOURCE_PREFIX_LEN + 1, -1)
def short_name(nt_uri):
"""Remove the < and > URI markers and the common URI prefix"""
return nt_uri[SHORTNAME_SLICE]
def get_redirects(redirects_filename):
"""Parse the redirections and build a transitively closed map out of it"""
redirects = {}
print("Parsing the NT redirect file")
for l, line in enumerate(BZ2File(redirects_filename)):
split = line.split()
if len(split) != 4:
print("ignoring malformed line: " + line)
continue
redirects[short_name(split[0])] = short_name(split[2])
if l % 1000000 == 0:
print("[%s] line: %08d" % (datetime.now().isoformat(), l))
# compute the transitive closure
print("Computing the transitive closure of the redirect relation")
for l, source in enumerate(redirects.keys()):
transitive_target = None
target = redirects[source]
seen = {source}
while True:
transitive_target = target
target = redirects.get(target)
if target is None or target in seen:
break
seen.add(target)
redirects[source] = transitive_target
if l % 1000000 == 0:
print("[%s] line: %08d" % (datetime.now().isoformat(), l))
return redirects
Вычисление матрицы смежности#
def get_adjacency_matrix(redirects_filename, page_links_filename, limit=None):
"""Extract the adjacency graph as a scipy sparse matrix
Redirects are resolved first.
Returns X, the scipy sparse adjacency matrix, redirects as python
dict from article names to article names and index_map a python dict
from article names to python int (article indexes).
"""
print("Computing the redirect map")
redirects = get_redirects(redirects_filename)
print("Computing the integer index map")
index_map = dict()
links = list()
for l, line in enumerate(BZ2File(page_links_filename)):
split = line.split()
if len(split) != 4:
print("ignoring malformed line: " + line)
continue
i = index(redirects, index_map, short_name(split[0]))
j = index(redirects, index_map, short_name(split[2]))
links.append((i, j))
if l % 1000000 == 0:
print("[%s] line: %08d" % (datetime.now().isoformat(), l))
if limit is not None and l >= limit - 1:
break
print("Computing the adjacency matrix")
X = sparse.lil_matrix((len(index_map), len(index_map)), dtype=np.float32)
for i, j in links:
X[i, j] = 1.0
del links
print("Converting to CSR representation")
X = X.tocsr()
print("CSR conversion done")
return X, redirects, index_map
# stop after 5M links to make it possible to work in RAM
X, redirects, index_map = get_adjacency_matrix(
redirects_filename, page_links_filename, limit=5000000
)
names = {i: name for name, i in index_map.items()}
Вычисление главного сингулярного вектора с использованием рандомизированного SVD#
print("Computing the principal singular vectors using randomized_svd")
t0 = time()
U, s, V = randomized_svd(X, 5, n_iter=3)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
# print the names of the wikipedia related strongest components of the
# principal singular vector which should be similar to the highest eigenvector
print("Top wikipedia pages according to principal singular vectors")
pprint([names[i] for i in np.abs(U.T[0]).argsort()[-10:]])
pprint([names[i] for i in np.abs(V[0]).argsort()[-10:]])
Вычисление оценок центральности#
def centrality_scores(X, alpha=0.85, max_iter=100, tol=1e-10):
"""Power iteration computation of the principal eigenvector
This method is also known as Google PageRank and the implementation
is based on the one from the NetworkX project (BSD licensed too)
with copyrights by:
Aric Hagberg Связанные примеры
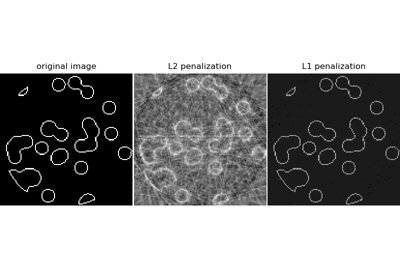
Компрессионное зондирование: реконструкция томографии с априорным распределением L1 (Lasso)
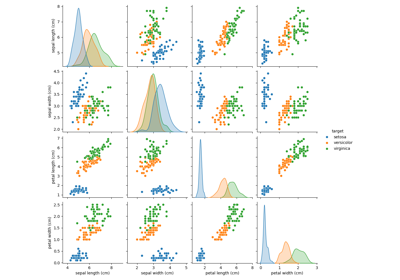
Анализ главных компонент (PCA) на наборе данных Iris

Сегментация изображения греческих монет на регионы
