Примечание
Перейти в конец чтобы скачать полный пример кода или запустить этот пример в браузере через JupyterLite или Binder.
Ковариации GMM#
Демонстрация нескольких типов ковариаций для гауссовских смесей.
См. Гауссовские смеси моделей для получения дополнительной информации об оценщике.
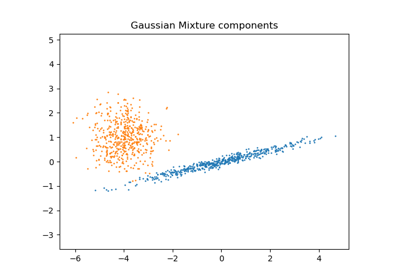
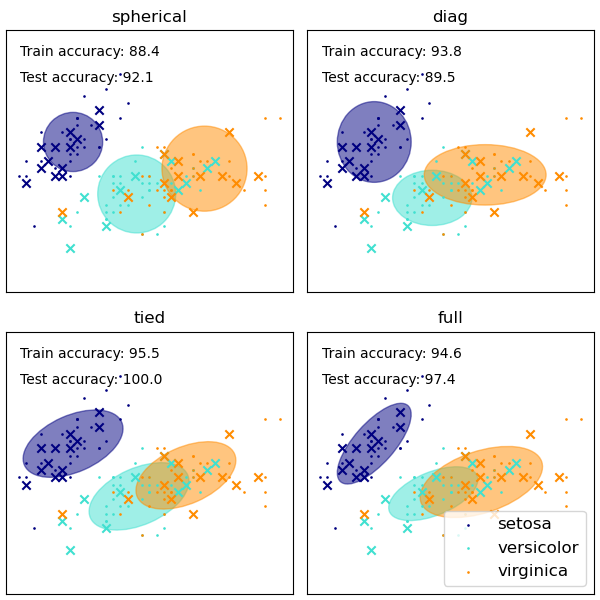
Хотя GMM часто используются для кластеризации, мы можем сравнить полученные кластеры с фактическими классами из набора данных. Мы инициализируем средние значения Гауссовых распределений средними значениями классов из обучающего набора, чтобы сделать это сравнение корректным.
Мы строим предсказанные метки как на обучающих, так и на отложенных тестовых данных, используя различные типы ковариаций GMM на наборе данных iris. Мы сравниваем GMM со сферическими, диагональными, полными и связанными ковариационными матрицами в порядке возрастания производительности. Хотя можно ожидать, что полная ковариация будет работать лучше в целом, она склонна к переобучению на небольших наборах данных и плохо обобщается на отложенные тестовые данные.
На графиках обучающие данные показаны точками, а тестовые данные - крестиками. Набор данных iris является четырехмерным. Здесь показаны только первые два измерения, поэтому некоторые точки разделены в других измерениях.
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.mixture import GaussianMixture
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
colors = ["navy", "turquoise", "darkorange"]
def make_ellipses(gmm, ax):
for n, color in enumerate(colors):
if gmm.covariance_type == "full":
covariances = gmm.covariances_[n][:2, :2]
elif gmm.covariance_type == "tied":
covariances = gmm.covariances_[:2, :2]
elif gmm.covariance_type == "diag":
covariances = np.diag(gmm.covariances_[n][:2])
elif gmm.covariance_type == "spherical":
covariances = np.eye(gmm.means_.shape[1]) * gmm.covariances_[n]
v, w = np.linalg.eigh(covariances)
u = w[0] / np.linalg.norm(w[0])
angle = np.arctan2(u[1], u[0])
angle = 180 * angle / np.pi # convert to degrees
v = 2.0 * np.sqrt(2.0) * np.sqrt(v)
ell = mpl.patches.Ellipse(
gmm.means_[n, :2], v[0], v[1], angle=180 + angle, color=color
)
ell.set_clip_box(ax.bbox)
ell.set_alpha(0.5)
ax.add_artist(ell)
ax.set_aspect("equal", "datalim")
iris = datasets.load_iris()
# Break up the dataset into non-overlapping training (75%) and testing
# (25%) sets.
skf = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=4)
# Only take the first fold.
train_index, test_index = next(iter(skf.split(iris.data, iris.target)))
X_train = iris.data[train_index]
y_train = iris.target[train_index]
X_test = iris.data[test_index]
y_test = iris.target[test_index]
n_classes = len(np.unique(y_train))
# Try GMMs using different types of covariances.
estimators = {
cov_type: GaussianMixture(
n_components=n_classes, covariance_type=cov_type, max_iter=20, random_state=0
)
for cov_type in ["spherical", "diag", "tied", "full"]
}
n_estimators = len(estimators)
plt.figure(figsize=(3 * n_estimators // 2, 6))
plt.subplots_adjust(
bottom=0.01, top=0.95, hspace=0.15, wspace=0.05, left=0.01, right=0.99
)
for index, (name, estimator) in enumerate(estimators.items()):
# Since we have class labels for the training data, we can
# initialize the GMM parameters in a supervised manner.
estimator.means_init = np.array(
[X_train[y_train == i].mean(axis=0) for i in range(n_classes)]
)
# Train the other parameters using the EM algorithm.
estimator.fit(X_train)
h = plt.subplot(2, n_estimators // 2, index + 1)
make_ellipses(estimator, h)
for n, color in enumerate(colors):
data = iris.data[iris.target == n]
plt.scatter(
data[:, 0], data[:, 1], s=0.8, color=color, label=iris.target_names[n]
)
# Plot the test data with crosses
for n, color in enumerate(colors):
data = X_test[y_test == n]
plt.scatter(data[:, 0], data[:, 1], marker="x", color=color)
y_train_pred = estimator.predict(X_train)
train_accuracy = np.mean(y_train_pred.ravel() == y_train.ravel()) * 100
plt.text(0.05, 0.9, "Train accuracy: %.1f" % train_accuracy, transform=h.transAxes)
y_test_pred = estimator.predict(X_test)
test_accuracy = np.mean(y_test_pred.ravel() == y_test.ravel()) * 100
plt.text(0.05, 0.8, "Test accuracy: %.1f" % test_accuracy, transform=h.transAxes)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.title(name)
plt.legend(scatterpoints=1, loc="lower right", prop=dict(size=12))
plt.show()
Общее время выполнения скрипта: (0 минут 0.254 секунды)
Связанные примеры