Примечание
Перейти в конец чтобы скачать полный пример кода или запустить этот пример в браузере через JupyterLite или Binder.
Пример распознавания лиц с использованием собственных лиц и SVM#
Набор данных, используемый в этом примере, представляет собой предобработанный отрывок из «Labeled Faces in the Wild», также известного как LFW: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/jessicali9530/lfw-dataset
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
from time import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import loguniform
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_lfw_people
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.metrics import ConfusionMatrixDisplay, classification_report
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV, train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.svm import SVC
Загрузите данные, если они еще не на диске, и загрузите их как массивы numpy
lfw_people = fetch_lfw_people(min_faces_per_person=70, resize=0.4)
# introspect the images arrays to find the shapes (for plotting)
n_samples, h, w = lfw_people.images.shape
# for machine learning we use the 2 data directly (as relative pixel
# positions info is ignored by this model)
X = lfw_people.data
n_features = X.shape[1]
# the label to predict is the id of the person
y = lfw_people.target
target_names = lfw_people.target_names
n_classes = target_names.shape[0]
print("Total dataset size:")
print("n_samples: %d" % n_samples)
print("n_features: %d" % n_features)
print("n_classes: %d" % n_classes)
Total dataset size:
n_samples: 1288
n_features: 1850
n_classes: 7
Разделить на обучающий набор и тестовый набор, оставив 25% данных для тестирования.
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42
)
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
Вычисление PCA (собственных лиц) на наборе данных лиц (рассматриваемом как неразмеченный набор данных): извлечение признаков без учителя / уменьшение размерности
n_components = 150
print(
"Extracting the top %d eigenfaces from %d faces" % (n_components, X_train.shape[0])
)
t0 = time()
pca = PCA(n_components=n_components, svd_solver="randomized", whiten=True).fit(X_train)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
eigenfaces = pca.components_.reshape((n_components, h, w))
print("Projecting the input data on the eigenfaces orthonormal basis")
t0 = time()
X_train_pca = pca.transform(X_train)
X_test_pca = pca.transform(X_test)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
Extracting the top 150 eigenfaces from 966 faces
done in 0.100s
Projecting the input data on the eigenfaces orthonormal basis
done in 0.006s
Обучить модель классификации SVM
print("Fitting the classifier to the training set")
t0 = time()
param_grid = {
"C": loguniform(1e3, 1e5),
"gamma": loguniform(1e-4, 1e-1),
}
clf = RandomizedSearchCV(
SVC(kernel="rbf", class_weight="balanced"), param_grid, n_iter=10
)
clf = clf.fit(X_train_pca, y_train)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
print("Best estimator found by grid search:")
print(clf.best_estimator_)
Fitting the classifier to the training set
done in 6.191s
Best estimator found by grid search:
SVC(C=np.float64(76823.03433306457), class_weight='balanced',
gamma=np.float64(0.0034189458230957995))
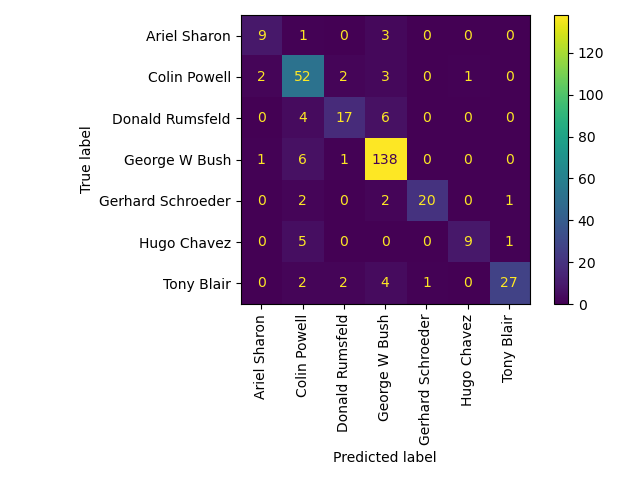
Количественная оценка качества модели на тестовом наборе
print("Predicting people's names on the test set")
t0 = time()
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test_pca)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred, target_names=target_names))
ConfusionMatrixDisplay.from_estimator(
clf, X_test_pca, y_test, display_labels=target_names, xticks_rotation="vertical"
)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Predicting people's names on the test set
done in 0.046s
precision recall f1-score support
Ariel Sharon 0.75 0.69 0.72 13
Colin Powell 0.72 0.87 0.79 60
Donald Rumsfeld 0.77 0.63 0.69 27
George W Bush 0.88 0.95 0.91 146
Gerhard Schroeder 0.95 0.80 0.87 25
Hugo Chavez 0.90 0.60 0.72 15
Tony Blair 0.93 0.75 0.83 36
accuracy 0.84 322
macro avg 0.84 0.75 0.79 322
weighted avg 0.85 0.84 0.84 322
Качественная оценка предсказаний с использованием matplotlib
def plot_gallery(images, titles, h, w, n_row=3, n_col=4):
"""Helper function to plot a gallery of portraits"""
plt.figure(figsize=(1.8 * n_col, 2.4 * n_row))
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0, left=0.01, right=0.99, top=0.90, hspace=0.35)
for i in range(n_row * n_col):
plt.subplot(n_row, n_col, i + 1)
plt.imshow(images[i].reshape((h, w)), cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.title(titles[i], size=12)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
построить график результата предсказания на части тестового набора
def title(y_pred, y_test, target_names, i):
pred_name = target_names[y_pred[i]].rsplit(" ", 1)[-1]
true_name = target_names[y_test[i]].rsplit(" ", 1)[-1]
return "predicted: %s\ntrue: %s" % (pred_name, true_name)
prediction_titles = [
title(y_pred, y_test, target_names, i) for i in range(y_pred.shape[0])
]
plot_gallery(X_test, prediction_titles, h, w)

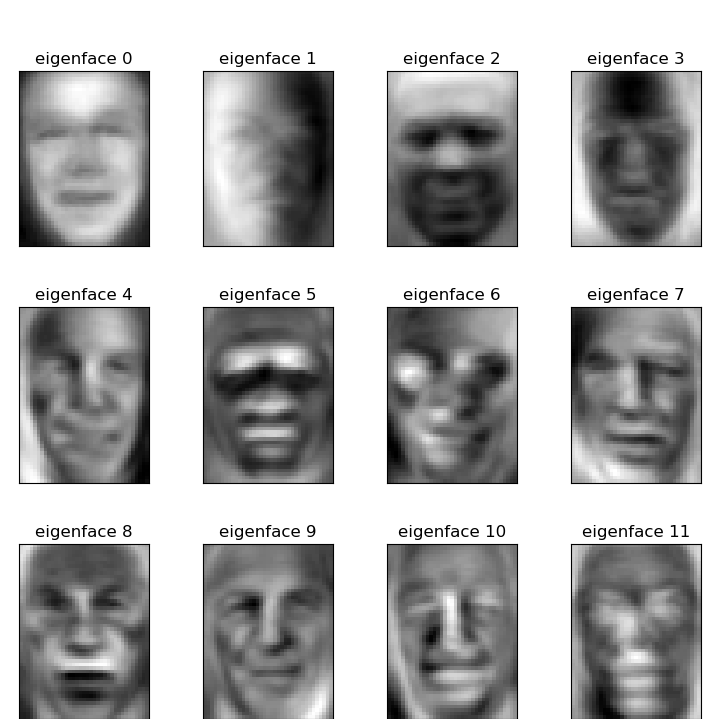
построить галерею наиболее значимых собственных лиц
eigenface_titles = ["eigenface %d" % i for i in range(eigenfaces.shape[0])]
plot_gallery(eigenfaces, eigenface_titles, h, w)
plt.show()

Проблема распознавания лиц была бы гораздо эффективнее решена обучением сверточных нейронных сетей, но это семейство моделей выходит за рамки библиотеки scikit-learn. Заинтересованным читателям следует попробовать использовать pytorch или tensorflow для реализации таких моделей.
Общее время выполнения скрипта: (0 минут 6.994 секунд)
Связанные примеры

Классификация текстовых документов с использованием разреженных признаков