Примечание
Перейти в конец чтобы скачать полный пример кода или запустить этот пример в браузере через JupyterLite или Binder.
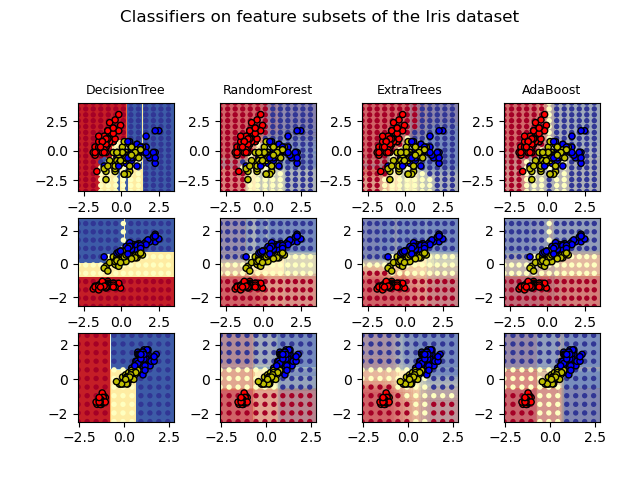
Построить поверхности решений ансамблей деревьев на наборе данных ирисов#
Построить поверхности решений лесов рандомизированных деревьев, обученных на парах признаков набора данных ирисов.
Этот график сравнивает поверхности решений, изученные классификатором дерева решений (первый столбец), классификатором случайного леса (второй столбец), классификатором экстра-деревьев (третий столбец) и классификатором AdaBoost (четвертый столбец).
В первой строке классификаторы построены с использованием только признаков ширины чашелистика и длины чашелистика, во второй строке — только длины лепестка и длины чашелистика, а в третьей строке — только ширины лепестка и длины лепестка.
В порядке убывания качества, при обучении (вне этого примера) на всех 4 признаках с использованием 30 оценщиков и оценке с помощью 10-кратной перекрестной проверки, мы видим:
ExtraTreesClassifier() # 0.95 score
RandomForestClassifier() # 0.94 score
AdaBoost(DecisionTree(max_depth=3)) # 0.94 score
DecisionTree(max_depth=None) # 0.94 score
Увеличение max_depth для AdaBoost снижает стандартное отклонение
оценок (но средняя оценка не улучшается).
Смотрите вывод консоли для дополнительных деталей о каждой модели.
В этом примере вы можете попробовать:
изменять
max_depthдляDecisionTreeClassifierиAdaBoostClassifier, возможно, попробуйтеmax_depth=3дляDecisionTreeClassifierилиmax_depth=NoneдляAdaBoostClassifierварьировать
n_estimators
Стоит отметить, что RandomForests и ExtraTrees можно обучать параллельно на многих ядрах, так как каждое дерево строится независимо от других. Образцы AdaBoost строятся последовательно и поэтому не используют несколько ядер.
DecisionTree with features [0, 1] has a score of 0.9266666666666666
RandomForest with 30 estimators with features [0, 1] has a score of 0.9266666666666666
ExtraTrees with 30 estimators with features [0, 1] has a score of 0.9266666666666666
AdaBoost with 30 estimators with features [0, 1] has a score of 0.82
DecisionTree with features [0, 2] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
RandomForest with 30 estimators with features [0, 2] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
ExtraTrees with 30 estimators with features [0, 2] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
AdaBoost with 30 estimators with features [0, 2] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
DecisionTree with features [2, 3] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
RandomForest with 30 estimators with features [2, 3] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
ExtraTrees with 30 estimators with features [2, 3] has a score of 0.9933333333333333
AdaBoost with 30 estimators with features [2, 3] has a score of 0.9866666666666667
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.ensemble import (
AdaBoostClassifier,
ExtraTreesClassifier,
RandomForestClassifier,
)
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
# Parameters
n_classes = 3
n_estimators = 30
cmap = plt.cm.RdYlBu
plot_step = 0.02 # fine step width for decision surface contours
plot_step_coarser = 0.5 # step widths for coarse classifier guesses
RANDOM_SEED = 13 # fix the seed on each iteration
# Load data
iris = load_iris()
plot_idx = 1
models = [
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=None),
RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=n_estimators),
ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators=n_estimators),
AdaBoostClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3), n_estimators=n_estimators),
]
for pair in ([0, 1], [0, 2], [2, 3]):
for model in models:
# We only take the two corresponding features
X = iris.data[:, pair]
y = iris.target
# Shuffle
idx = np.arange(X.shape[0])
np.random.seed(RANDOM_SEED)
np.random.shuffle(idx)
X = X[idx]
y = y[idx]
# Standardize
mean = X.mean(axis=0)
std = X.std(axis=0)
X = (X - mean) / std
# Train
model.fit(X, y)
scores = model.score(X, y)
# Create a title for each column and the console by using str() and
# slicing away useless parts of the string
model_title = str(type(model)).split(".")[-1][:-2][: -len("Classifier")]
model_details = model_title
if hasattr(model, "estimators_"):
model_details += " with {} estimators".format(len(model.estimators_))
print(model_details + " with features", pair, "has a score of", scores)
plt.subplot(3, 4, plot_idx)
if plot_idx <= len(models):
# Add a title at the top of each column
plt.title(model_title, fontsize=9)
# Now plot the decision boundary using a fine mesh as input to a
# filled contour plot
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(
np.arange(x_min, x_max, plot_step), np.arange(y_min, y_max, plot_step)
)
# Plot either a single DecisionTreeClassifier or alpha blend the
# decision surfaces of the ensemble of classifiers
if isinstance(model, DecisionTreeClassifier):
Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
cs = plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cmap)
else:
# Choose alpha blend level with respect to the number
# of estimators
# that are in use (noting that AdaBoost can use fewer estimators
# than its maximum if it achieves a good enough fit early on)
estimator_alpha = 1.0 / len(model.estimators_)
for tree in model.estimators_:
Z = tree.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
cs = plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=estimator_alpha, cmap=cmap)
# Build a coarser grid to plot a set of ensemble classifications
# to show how these are different to what we see in the decision
# surfaces. These points are regularly space and do not have a
# black outline
xx_coarser, yy_coarser = np.meshgrid(
np.arange(x_min, x_max, plot_step_coarser),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, plot_step_coarser),
)
Z_points_coarser = model.predict(
np.c_[xx_coarser.ravel(), yy_coarser.ravel()]
).reshape(xx_coarser.shape)
cs_points = plt.scatter(
xx_coarser,
yy_coarser,
s=15,
c=Z_points_coarser,
cmap=cmap,
edgecolors="none",
)
# Plot the training points, these are clustered together and have a
# black outline
plt.scatter(
X[:, 0],
X[:, 1],
c=y,
cmap=ListedColormap(["r", "y", "b"]),
edgecolor="k",
s=20,
)
plot_idx += 1 # move on to the next plot in sequence
plt.suptitle("Classifiers on feature subsets of the Iris dataset", fontsize=12)
plt.axis("tight")
plt.tight_layout(h_pad=0.2, w_pad=0.2, pad=2.5)
plt.show()
Общее время выполнения скрипта: (0 минут 6.617 секунд)
Связанные примеры
Гауссовский процесс классификации (GPC) на наборе данных iris
Изменение регуляризации в многослойном перцептроне
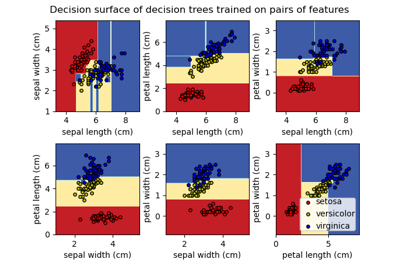
Построить поверхность решений деревьев решений, обученных на наборе данных ирисов